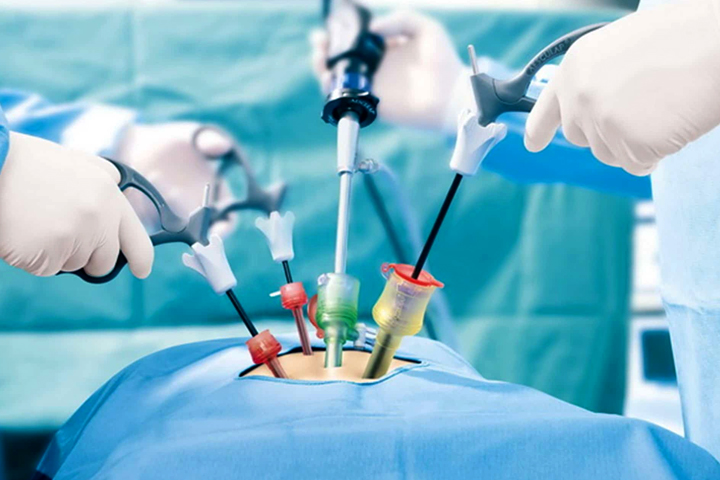
Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic surgery, also known as minimally invasive surgery, is a modern surgical technique that allows surgeons to perform various procedures with smaller incisions compared to traditional open surgery. It involves using a laparoscope, a thin, long tube with a camera and light source attached to its end. The laparoscope is inserted through small incisions in the body, providing a real-time view of the internal organs on a monitor.
During laparoscopic surgery, carbon dioxide gas is used to inflate the abdominal cavity, creating space for the surgeon to maneuver and visualize the organs clearly. Surgical instruments are then inserted through additional small incisions to perform the necessary procedures with precision and care.
Advantages of Laparoscopic Surgery:
- Smaller Incisions: Laparoscopic surgery requires only small incisions, resulting in reduced scarring, less pain, and faster healing compared to open surgery.
- Shorter Hospital Stay: Patients often experience shorter hospital stays and faster recovery times, allowing them to return to their normal activities sooner.
- Reduced Blood Loss: The smaller incisions in laparoscopic surgery typically lead to less blood loss during the procedure.
- Lower Risk of Infection: The risk of post-operative infections is generally lower in laparoscopic surgery due to the smaller incisions and reduced exposure of internal organs.
- Better Cosmetic Outcome: The smaller scars from laparoscopic surgery are more cosmetically appealing than the larger scars from open surgery.
Laparoscopic surgery is used in various medical specialties, including gynecology, general surgery, urology, and gastroenterology. Some common gynecological procedures performed laparoscopically include:
- Laparoscopic hysterectomy (removal of the uterus).
- Laparoscopic myomectomy (removal of uterine fibroids).
- Laparoscopic ovarian cystectomy (removal of ovarian cysts).
- Laparoscopic treatment of endometriosis.
- Laparoscopic tubal ligation (female sterilization).
It's important to note that not all surgical procedures can be performed laparoscopically, and the suitability of this approach depends on the specific case and the surgeon's expertise. Some complex or emergency cases may require open surgery for optimal outcomes.
Laparoscopic surgery is considered a safe and effective technique when performed by trained and experienced surgeons. Patients considering laparoscopic procedures should consult with their healthcare providers to discuss the benefits, risks, and suitability of this approach for their individual medical needs.